Behind every production line, every successful maintenance operation, and the smooth operation of the industrial supply chain lies one unseen yet vital element: the quality of MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Operations) master data. In the era of data-driven and automated industries, corporate companies can no longer afford to ignore the integrity of their material data. Especially in the Yogyakarta region, which is emerging as a strategic industrial ecosystem, the need for precise data structures is becoming increasingly urgent.
Strategic Perspective: Why MRO Data Is a Corporate Asset
In modern industrial environments, material master data is no longer just an administrative record. It is the backbone of logistics, procurement, maintenance, and compliance decisions. Mistakes in nomenclature, item duplication, or misclassification can create invisible costs that ripple from warehouse to finance, from operations to procurement.
Key Insights:
- Data is a lever for multi-departmental efficiency: Material data quality has a direct impact on procurement lead time, planning accuracy, and maintenance effectiveness.
- Without standard data, digitalization is just an illusion.: ERP, EAM, or CMMS systems will only replicate chaos if the input data is unstructured.
- Improving readiness audits and transparency: Amidst demands for ESG and good corporate governance, companies are required to be transparent down to the granularity of material data.
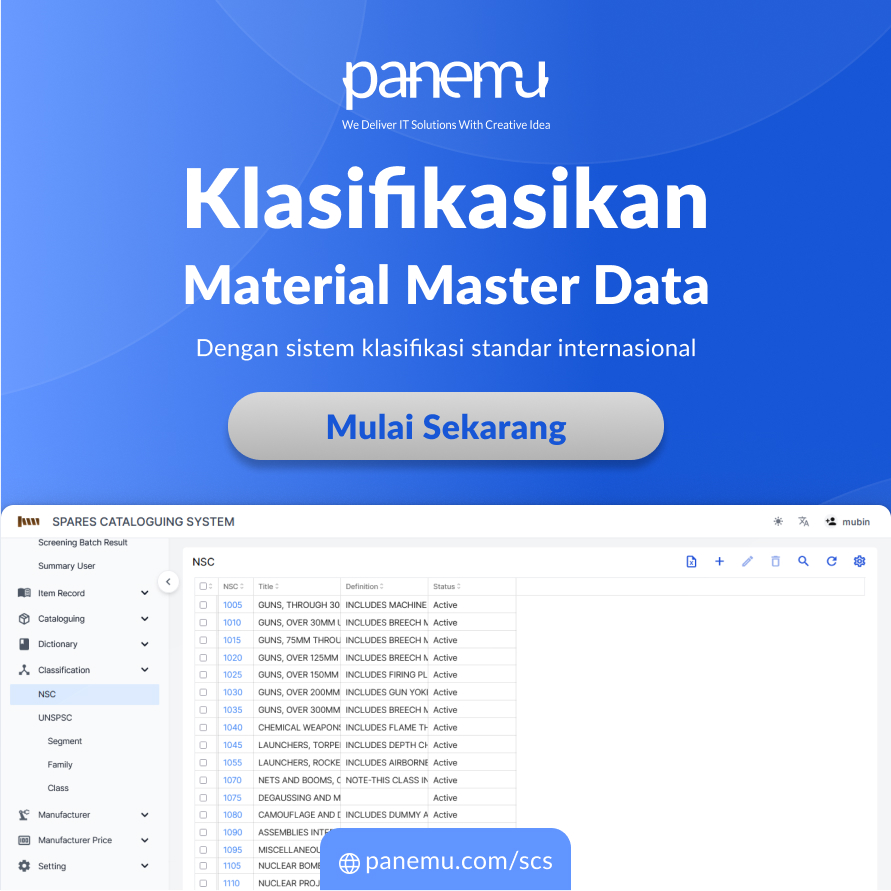
What is MRO Master Data Cataloging?
Cataloguing is a systematic process of standardizing, reorganizing, and cleansing material master data based on industry taxonomies such asUNSPSC (United Nations Standard Products and Services Code), Nato Codification System (NCS), and internal corporate structure.
More than just organizing item names, cataloguing creates an intelligent classification system that makes each data entity:
- Uniquely identified
- Can be searched quickly and precisely
- Can be utilized across functions and systems
Real Challenges of Industry in Yogyakarta
The Yogyakarta region is growing as a national industrial hub—including manufacturing, energy, mining, construction, logistics, and public services. However, nearly all sectors face similar challenges:
Strategic Barriers:
- Unstandardized data legacy: Legacy material with inconsistent format and difficult to migrate.
- Item duplication and free naming: Causes wasteful procurement and accumulation of dead stock.
- Absence of governance taxonomy: There is no standard classification policy between divisions.
- Data silos between departments: Procurement, engineering, and warehouse work with different item definitions.
Ideal Structure in Cataloguing Master Data
Professional cataloging refers to a layered structure that facilitates comprehensive data identification, analysis, and integration. These include:
Critical Components:
- Unique Material Code (Material Master Number)
- Validated Technical Description (Standard Item Description)
- Multilevel Classification (UNSPSC, NCS, Internal Categories)
- Technical & Commercial Parameters (Specifications, Brand, Unit, Location of Use)
- Status Obsolescence dan Criticality
This structure allows companies to consolidate vendors, optimize stock, and map supply chain risks more precisely.
Functional Use Cases: When Cataloguing Provides Strategic Value
📌 Use Case 1: Renewable Energy Factory
The company experienced procurement waste because 1,200 spare parts with different names actually referred to 380 identical items. After cataloging, budget savings reached 15% in a single budget cycle.
📌 Use Case 2: Construction and Infrastructure Holding
The holding company, with six subsidiaries, has separate material master systems. Cataloging unifies everything into a single taxonomy, enabling volume negotiations with vendors nationwide.
📌 Use Case 3: Engineering Education Institutions in Yogyakarta
Mechanical engineering laboratories struggle with instrument calibration and traceability. Cataloging implementation allows visibility into the technical specifications of student practice equipment.
Relevant Implementation Strategies for Corporations in Yogyakarta
Every company has its own data complexities and culture. Therefore, cataloging implementation must be agile and results-oriented.
Effective Framework:
- Data Profiling & Initial Audit: Measures the health and corruption of existing data.
- Definition of Taxonomy Structure According to Sector: Including adjustments to NCS, UNSPSC, or custom taxonomy.
- Collaborative Workshop: Involve engineering, logistics, and procurement functions to validate the description.
- Implementation of Governance Rule Set: Standards for naming, units, languages, and data formats.
- Migration and Revalidation: Transfer data to ERP/CMMS systems in a clean and validated manner.
Long-Term Impacts That Cannot Be Ignored
Cataloguing is not a one-time project, but a cornerstone of long-term data transformation.
Direct & Indirect Impact:
- Increase stock accuracy up to >95%
- Reduction of material redundancy >30%
- Vendor consolidation and stronger price negotiations
- Data visibility for risk planning and ESG reporting
- Full alignment between engineering, logistics and procurement
Why Panemu is the MRO Data Transformation Partner You Need
As a service provider that understands the dynamics of the corporate industrial sector,The opinionpresentCataloguing Servicedesigned to address fundamental and strategic issues in your company's material data.
This service isn't just about technical matters, but also integrates cross-functional understanding: engineering, supply chain, asset management, and compliance. We utilize a global framework but adapt it to the local context in Yogyakarta.
Learn how we can help you transform your MRO data into a competitive advantage:
In the era of data-driven industries, the biggest mistake is ignoring the little messes in master data. Let's make your MRO data not just clean, but strategic. With Panemu, you're building more than just a data structure—you're building a more efficient, connected future, ready to face the challenges of Industry 4.0.